使用寿命计算公式
The formulas for calculating service life
对于滚子和滚针 (For rollers and needles)
对于钢球 (For balls)
a = 事件概率因子 (Event probability factor)
Ceff = 每个滚动元件的有效承载能力 (N)
P = 动态当量载荷 (N)
L = 标称使用寿命 (m)
事件概率因子 a
Event probability factor a
滚子接触轴承的承载能力符合 DIN ISO 标准。这代表使用寿命计算中的一个值,在导轨的操作使用期间,有 90% 的概率超过此值。
如果前面提到的理论使用寿命概率因子 90% 不足够,则需要通过因子 a 调整使用寿命值。
| 事件概率 (%) Event probability in % | 90 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 因子 a Factor a | 1 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0.21 |
有效承载能力 Ceff
Effective load carrying capacity Ceff
外部影响(例如轨道硬度和温度)可能会降低承载能力 C,这意味著需要计算 Ceff。
Ceff = 每个滚动元件的有效承载能力 (N)
Effective load carrying capacity per rolling element in N
fH = 硬度因子
Hardness factor
fT = 温度因子
Temperature factor
C = 每个滚动元件的最大允许承载能力 (N)
Max. permissible load carrying capacity per rolling element in N
硬度因子 fH
Hardness factor fH
无摩擦导轨中偏离标准条件(HRC 58-62)的材料可以用因子 fH 记录:
| 轨道硬度 (HRC) Track hardness in HRC | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58-62 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硬度因子 fH Hardness factor fH | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 1 |
温度因子 fT
Temperature factor fT
增加的温度会影响操作条件(材料特性),必须使用因子 fT 考虑。
| 导轨温度 (°C) Temperature of the guideway in °C | ≤ 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度因子 fT Temperature factor fT | 1 | 0.9 | 0.75 | 0.6 |
Ceff 计算范例
Example calculation for Ceff
给定条件:
- 导轨型号 R6
- 硬度 58-62 HRC ⇒ fH = 1
- 温度 200°C ⇒ fT = 0.9
- 滑架 AA 6 ⇒ C = 530 N(每个滚子)
动态当量载荷 P
Dynamically equivalent load P
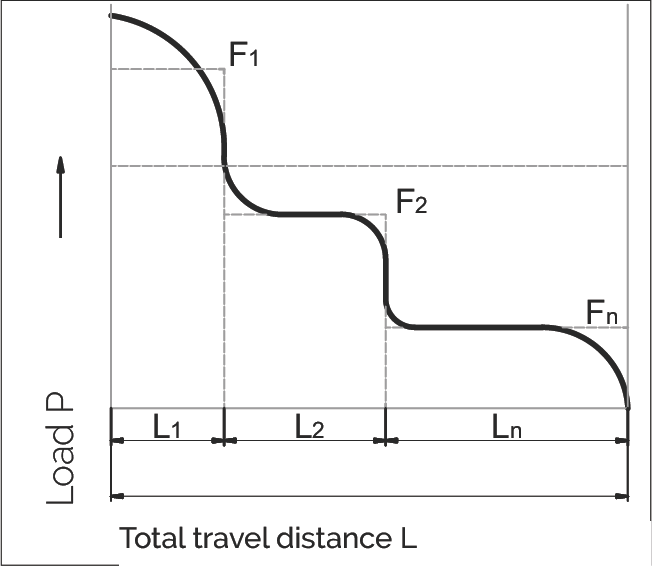
作用在直线导轨系统上的负载 (F) 在操作期间会受到频繁波动。在计算使用寿命时应考虑这种情况。在行程距离期间,不同操作条件下导轨的不同负载吸收被描述为动态当量载荷 P。
阶梯负载 (Stepped load)
对于滚子和滚针:
对于钢球:
正弦负载 (Sinusoidal load)
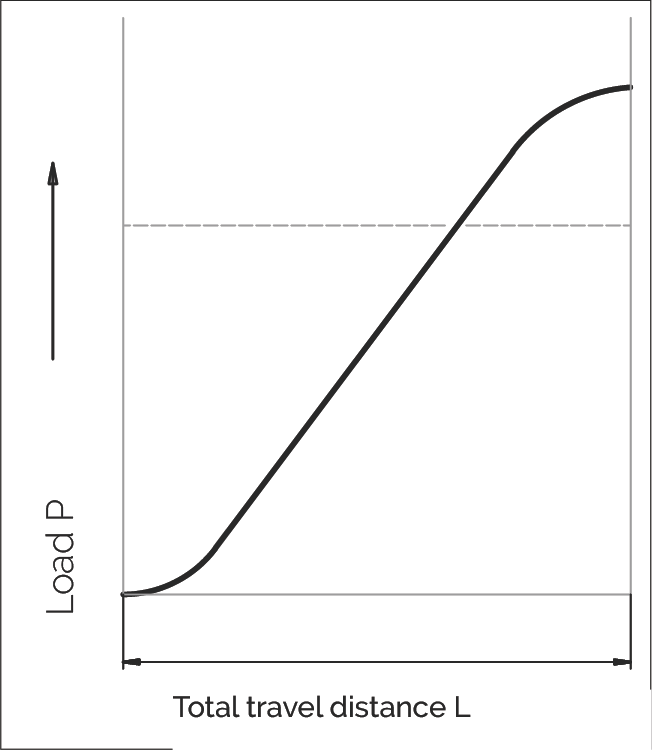
P = 当量载荷 (N)
F₁...Fn = 部分行程距离 L₁...Ln 期间的单独负载 (N)
Fmax = 最大负载 (N)
L = L₁ + ... + Ln = 一个负载循环期间的总行程 (mm)
L₁...Ln = 负载循环期间单独负载的部分行程距离 (mm)
使用寿命计算范例
Service Life Calculation Example
范例:RNG 6-300 直线导轨配 KBN 6 滑架
Example calculation with a linear guideway of type RNG 6-300 with KBN 6 cage
1. 给定条件 (Given Conditions)
| 事件概率 (Event Probability) | 97%,对应因子 a = 0.44 |
| 滚子额定动载荷 (Dynamic Load Capacity per Roller) | 1,800 N |
| 滚子数量 (Number of Rollers) | 16 个 |
| 导轨总承载能力 (Total Guideway Load Capacity) | 16 × 1,800 N = 28,800 N |
| 应用负载 (Applied Load) | P = 10,000 N |
2. 使用寿命计算(以米为单位)(Service Life Calculation in Meters)
使用公式:
代入数值:
计算结果:
L = 1,495,412 m
Service life ≈ 1.5 million meters
3. 转换为使用小时数 (Conversion to Operating Hours)
如果需要以小时为单位表示使用寿命,需要知道以下参数:
- H = 每次行程的距离(米)
- t = 完成一次行程所需的时间(秒)
使用寿命(小时)计算公式:
说明:
• 分母中的 3,600 是将秒转换为小时的换算系数
• Lh 的结果单位为小时 (hours)
• 此公式假设恒定的运动速度和负载条件
4. 计算范例(转换为小时)(Example: Conversion to Hours)
假设工作条件:
- 行程距离 H = 2 m
- 行程时间 t = 5 秒
计算结果:
Lh ≈ 1,038 小时
Operating life ≈ 1,038 hours
修正因子 Rtmin
The correction factor Rtmin
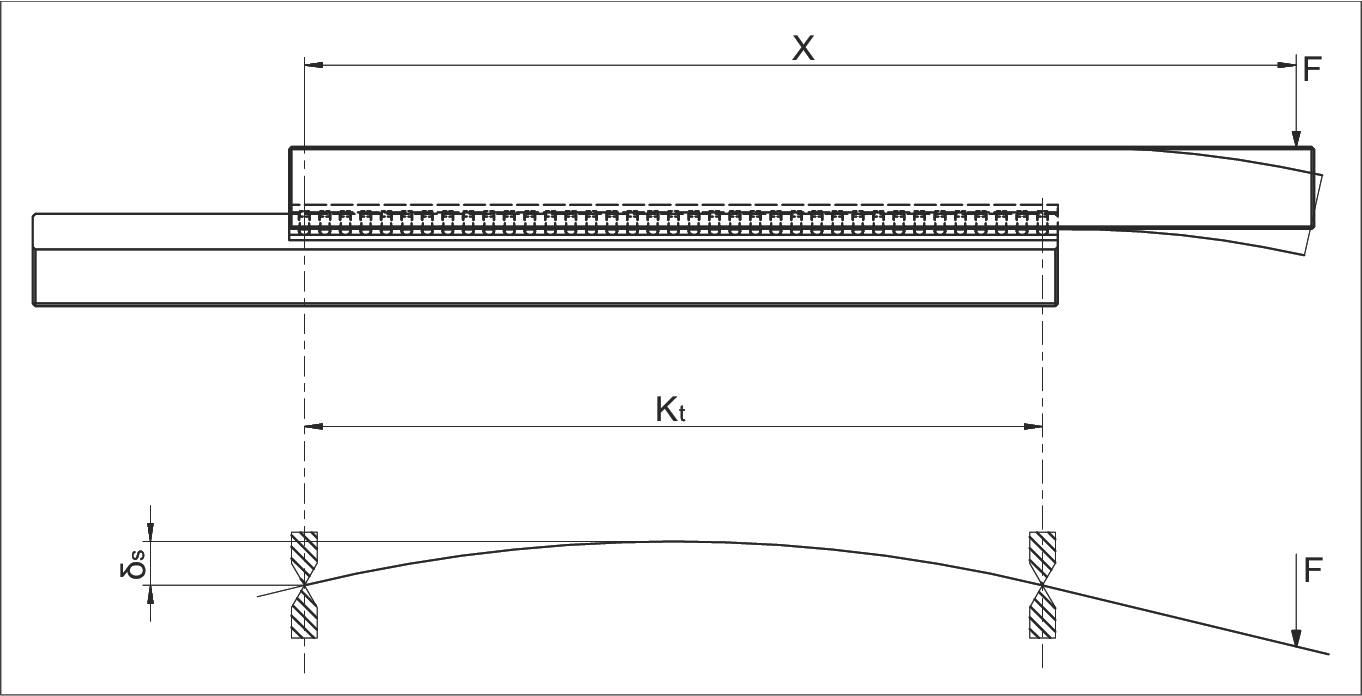
在前面的章节中,我们说明了如何根据给定的承载能力和实际负载来计算使用寿命。在此过程中,必须考虑每个滑架的负载滚动元件数量 (Rt)。
同样重要的是评估周围结构在向无摩擦导轨传递力时的行为。弹性变形或机床中的几何误差会导致只有一部分安装的滚动元件能有效地吸收负载。
对于这个与应用相关的问题,通常很难做出可靠的判断,例如通过对功能模型进行量测或使用基于有限元方法的计算。因此,通常采取简化措施进行尺寸计算,即使用修正因子 Rtmin 将外部负载分配到较少的滚动元件上。
确定 Rtmin
Determining Rtmin
要确定 Rtmin,首先必须根据历史经验评估连接结构的刚度:
A = 刚度结构 (Rigid structure)
B = 正常结构 (Normal structure)
参数说明
Parameter Definitions
| δS | 连接结构的变形量 (µm) | Deformation of the connecting structure in µm |
| δA | 滚动元件包括导轨的变形量 (µm) | Deformation of the rolling element including the guide rail in µm (see chapter 12.5) |
| F | 负载 (N) | Load in N |
| X | X 轴上的杠杆臂距离 (mm) | Lever arm distance on x-axis in mm |
| Kt | 负载滑架的长度 (mm) | Load-bearing cage length in mm |
| Rt | 负载滚动元件的数量 | Number of load-bearing rollers |
| Rtmin | 修正因子 | Correction factor |
Rtmin 计算图表
Chart for Calculating Rtmin

图表说明:
- 曲线 A:刚度结构 (Rigid structure)
- 曲线 B:正常结构 (Normal structure)
- 横轴:X/Kt 比值
- 纵轴:Rt 值(Rt/2、Rt/4 等)
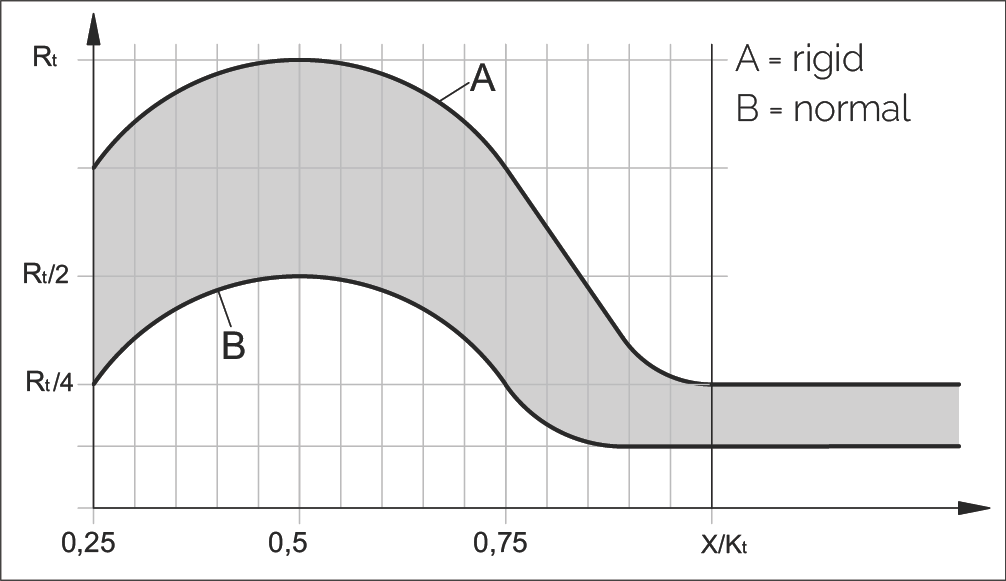
根据图表计算 Rtmin
To calculate Rtmin according to the diagram applies
| 结构类型 Structure | A(刚度) A (rigid) | B(正常) B (normal) |
|---|---|---|
| X > Kt | Rtmin to Rt/4 | Rtmin |
| X < Kt | 根据图表 (as per diagram) | 根据图表 (as per diagram) |
不同滚动元件类型的 Rtmin 值
Rtmin Values for Different Rolling Element Types
| For Rtmin, the following applies | 滚动元件类型 Rolling element type | 滑架型号 Cage types |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 钢球 (Balls) | AK |
| 1 | 滚子 (Rollers) | AA, AC, EE, KBN and KBS |
| 5 | 滚针 (Needles) | SHW and HW |
| 0.5 | 循环单元(滚子) Recirculating unit with rollers | SR and NRT |
| 1 | 循环单元(钢球) Recirculating unit with balls | SK, SKD and SKC |
计算范例
Calculation Examples
范例计算 1:直线导轨 R6 配滑架 AK 6/20
Example calculation no. 1: Linear guideway R6 with cage type AK 6/20
给定条件:
- X = 200 mm
- Kt = 171 mm
- 因此使用计算方法:X > Kt
分析:
直线导轨水平排列,因此适用以下条件:
刚度结构的计算 (Calculation for a rigid structure)
- 根据表格,钢球的钢球计数 Rtmin to Rt/4 适用
- Rtmin 对应于 2 个钢球
- Rt/4 对应于 2.50 个钢球
正常结构的计算 (Calculation for a normal structure)
- 根据表格,Rtmin 适用
- Rtmin 对应于 2 个钢球
范例计算 2:直线导轨 R6 配滑架 AK 6/11
Example calculation no. 2: Linear guideway R6 with cage type AK 6/11
给定条件:
- X = 75 mm
- Kt = 90 mm
- 因此使用计算方法:X < Kt
刚度结构的计算 (Calculation for a rigid structure)
根据图表,X = 0.83 of Kt (75 mm : 90 mm),因此 Rt/2
有 11 个负载钢球,结果为 5.5 个钢球 (11 个负载钢球 : 2)
正常结构的计算 (Calculation for a normal structure)
根据图表 Rt/8
有 11 个负载钢球,结果为 1.3 个钢球 (11 : 8)